Couldn’t grab the underlying principles of voice change even after years of learning? Try a logical, scientific approach as used in 70+ change the voice examples with answers.
By the way, why do you need to learn the change of voice? You’ll get the answer as you go through the 10 differences between active voice and passive voice.
The learner-oriented, logically explained change the voice examples with answers cover all tenses and sentence types.
There’re 4 sections.
1. Typical Example: 2 Ways to change the voice SHE GAVE ME FIVE FILMS.
2. 70+ Change the Voice Examples with Answers
3. Universal rules to change the voice.
4. 10 least-discussed differences between active and passive voice.
Did you know?
- The change of voice is much easier than dealing with the transition from direct to the indirect narration.
- You need not separately learn change the voice rules for each tense!
- The 70+ change the voice examples with answers from different tenses can be dealt with using a universal approach.
1. Typical Example: 2 Ways to change the voice SHE GAVE ME FIVE FILMS.
Look at the example illustrating two ways to change the voice SHE GAVE ME FIVE FILMS.
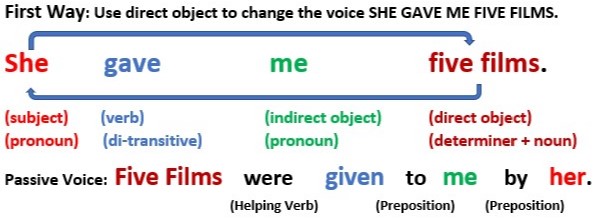
First way: Use direct object to change the voice SHE GAVE ME FIVE FILMS.
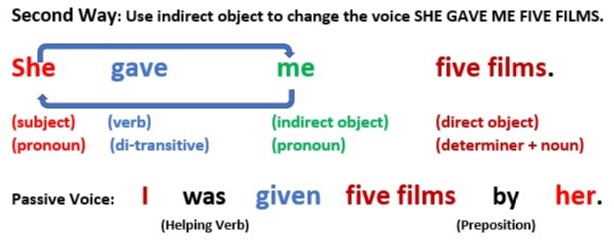
Second way: Use indirect object to change the voice SHE GAVE ME FIVE FILMS.
Explanation:
There are two ways for the ‘She gave me five films’ passive voice. That is, it can be converted into two different passive form sentences.
It is due to the presence of two objects, i.e. a direct object and an indirect object.
First, using the direct object (five films), its passive form will look like:
Five films were given to me by her.
Second, using the indirect object (me), the passive form will look like:
I was given five films by her.
Did you know why there are two objects in this sentence?
It is because the verb “give” is a di-transitive verb, i.e. it requires two objects. In other words, the action is passed on to two objects in this sentence.
For the further understanding of the concept, keep practicing change the voice examples with answers.
Also read: Score 8/8, Fast-to-Learn 9th Class English Letters Notes
2. 70+ Change the Voice Examples with Answers – All Tenses and Sentence Types
The more you practice the better you will have grip over the change of voice. Here are 70+ active and passive voice examples with answers and logical explanations.
Exercise 1: SHE GAVE ME FIVE BOOKS change the voice.
Answer: Five books were given to me by her.
Or
I was given five books by her.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 2: THEY ARE BUYING THEIR HOUSE passive form.
Answer: Their house is being bought by them.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Continuous Tense)
Exercise 3: WE SHALL HAVE KILLED A SNAKE change from active to passive.
Answer: A snake will have been killed by us.
(Affirmative Sentence – Future Perfect Tense)
Note: The sentence “We shall have killed a snake” also contains the elements of assumption, determination, and prediction. More passive voice exercises with answers will further strengthen your grip on this niche of grammar.
Exercise 4: Change the voice THEY HAVE NOT DONE THEIR JOB.
Answer: Their job has not been done by them.
(Negative Sentence – Present Perfect Tense)
Also read: Easiest, Best Scoring 9th Class English Question Answer Notes
Exercise 5: WHO IS KNOCKING AT THE DOOR? Change the voice.
Answer: By whom is the door being knocked at?
(Interrogative Sentence from WH family – Present Continuous Tense)
Exercise 6: POLISH MY SHOES change the voice.
Answer: Let my shoes be polished.
(Imperative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 7: HE WILL WRITE A LETTER.
Answer: A letter will be written by him.
(Affirmative Sentence – Future Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 8: DID HE RING THE BELL?
Answer: Was the bell rung by him?
(Interrogative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Also read: To-the-Point, Top Scoring 10th English Question Answer Notes
Exercise 9: HE WAS PLAYING FOOTBALL.
Answer: Football was being played by him.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Continuous Tense)
Exercise 10: THEY HAVE BOUGHT A HOUSE.
Answer: A house has been bought by them.
(Affirmative/Positive Sentence – Present Perfect Tense)
Exercise 11: SHE LIKES APPLES.
Answer: Apples are liked by her.
(Positive/Affirmative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 12: A CAR RAN OVER AN OLD MAN change the voice.
Answer: An old man was run over by a car.
(Affirmative/Positive Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 13: Change from active voice to passive voice THEY CAUGHT THE THIEF.
Answer: The thief was caught by them.
(Affirmative/Positive Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 14: THE BOARD HAD GIVEN ME A GOLD MEDAL.
Answer: A gold medal had been given to me by the board.
Or
I had been given a gold medal by the board.
(Positive/Affirmative Sentence – Past Perfect Tense)
Exercise 15: THE BOARD HAS GIVEN ME A GOLD MEDAL.
Answer: A gold medal has been given to me by the board.
Or
I have been given a gold medal by the board.
(Positive/Affirmative Sentence – Present Perfect Tense)
Exercise 16: WE DID NOT HEAR A SOUND change the voice from active to passive.
Answer: A sound was not heard by us.
(Negative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 17: EAT THESE APPLES.
Answer: Let these apples be eaten.
(Imperative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 18: SHE WAS TEACHING THE STUDENTS.
Answer: The students were being taught by her.
(Affirmative/Positive Sentence – Past Continuous Tense)
Exercise 19: THEY GAVE ME A PRIZE.
Answer: I am given a prize by them.
Or
A prize was given to me by them.
(Affirmative/Positive Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 20: HE HAS WRITTEN MANY POEMS change into the passive form.
Answer: Many poems have been written by him.
(Positive/Affirmative Sentence – Present Perfect Tense)
Exercise 21: THEY READ MANY BOOKS.
Answer: Many books are read by them.
(Affirmative/Positive Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 22: HE IS PLAYING A MATCH.
Answer: A match is being played by him.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Continuous Tense)
Exercise 23: THEY DID NOT HELP US.
Answer: We were not helped by them.
(Negative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 24: THE JUGGLER WILL SHOW FEATS.
Answer: Feats will be shown by the juggler.
(Positive Sentence – Future Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 25: HE DOES NOT DECEIVE ME.
Answer: I am not deceived by him.
(Negative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense:
Exercise 26: THE BOY MAKES THE PICTURE.
Answer: The picture is made by the boy.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 27: THE MOTHER DOES NOT LOVE THE CHILDREN.
Answer: The children are not loved by the mother.
(Negative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 28: THEY HAVE BOUGHT A HORSE.
Answer: A horse has been bought by them.
(Positive Sentence – Present Perfect Tense)
Exercise 29: OPEN THE DOOR.
Answer: Let the door be opened.
(Imperative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 30: PEOPLE WERE FLYING KITES.
Answer: Kites were being flown by people.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Continuous Tense)
Exercise 31: MY FRIENDS ARE ENCOURAGING ME.
Answer: I am being encouraged by my friends.
(Positive Sentence – Present Continuous Tense)
Exercise 32: I WROTE A LETTER.
Answer: A letter was written by me.
(Affirmative/Positive Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 33: SHUT THE DOOR.
Answer: Let the door be shut.
(Imperative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 34: HE READS GOOD BOOKS.
Answer: Good books are read by him.
(Positive Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 35: THEY ARE BUYING THIS HOUSE.
Answer: This house is being bought by them.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Continuous Tense)
Also read: Easiest Ever Question Answer B1-First Year English Notes
Exercise 36: THEY HAD GAINED NOTHING.
Answer: Nothing had been gained by them.
(Positive Sentence – Past Perfect Tense)
Exercise 37: THE DOOR OF THE CAR WAS OPENED BY THE DRIVER change the voice.
Answer: The driver opened the door of the car. (Active Voice)
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 38: WE SHALL HAVE KILLED THE SNAKE.
Answer: The snake will have been killed by us.
(Positive Sentence – Future Perfect Tense)
Exercise 39: THE SNAKE WILL HAVE BEEN KILLED BY US change the voice of the sentence.
Answer: We shall have killed the snake. (Active Voice)
(Positive Sentence – Future Perfect Tense)
Exercise 40: SHE WAS TEACHING THE STUDENTS.
Answer: The students were being taught by her.
(Positive Sentence – Past Continuous Tense)
Exercise 41: WHY IS HE MENDING THE CHAIR?
Answer: Why is the chair being mended by him?
(Interrogative Sentence from WH-family – Present Continuous Tense)
Exercise 42: SHE GAVE ME A PEN.
Answer: A pen was given to me by her.
Or
I was given a pen by her.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 43: WE USE MILK FOR MAKING CHEESE.
Answer: Milk is used by us for making cheese.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 44: THEY WILL PLAY HOCKEY. Change the voice.
Answer: Hockey will be played by them.
(Affirmative Sentence – Future Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 45: THE TEACHER WAS HELPING THE STUDENTS.
Answer: The students were being helped by the teacher.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Continuous Tense)
Exercise 46: THEY HAD NOT DONE THEIR HOME TASK.
Answer: Their home task had not been done by them.
(Negative Sentence – Past Perfect Tense)
Exercise 47: HE WILL GIVE ME A BOX OF CHOCOLATES.
Answer: I will be given a box of chocolates by him.
Or
A box of chocolates will be given to me by him.
(Affirmative Sentence – Future Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 48: THE SUDDEN NOISE FRIGHTENED THE CHILD.
Answer: The child was frightened by the sudden noise.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 49: WHEN DID SHE FIND IT?
Answer: When was it found by her?
(Interrogative Sentence using a question (WH) word – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 50: THE BOYS MAKE THE PICTURE.
Answer: The picture is made by the boys.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
You Might be Interested to Learn: 70+ Advantages of Internet in Points and Essay in Detail
Exercise 51: SHE HAS NOT BEATEN THE DOG.
Answer: The dog has not been beaten by them.
(Negative Sentence – Present Perfect Tense)
Exercise 52: THE BOY IS CLIMBING THE WALL.
Answer: The wall is being climbed by the boy.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Continuous Tense)
Exercise 53: HE TOOK AWAY MY BOOKS.
Answer: My books were taken away by him.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 54: HE IS WEARING NEW CLOTHES.
Answer: New clothes are being worn by him.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Continuous Tense)
Exercise 55: SONGS ARE SUNG BY HER change the voice.
Answer: She sings songs. (Active Voice)
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 56: THE BANK DOES NOT GIVE LOAN TO ME.
Answer: Loan is not given to me by the bank.
(Negative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 57: THEY ARE KILLING THE MAD DOGS.
Answer: The mad dogs are being killed by them.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Continuous Tense)
Exercise 58: HE HAS NOT THROWN ROTTEN EGGS.
Answer: Rotten eggs have not been thrown by him.
(Negative Sentence – Present Perfect Tense)
Exercise 59: WE HAD SEEN HIM.
Answer: He had been seen by us.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Perfect Tense)
Exercise 60: OUR TEAM WON THE MATCH.
Answer: The match was won by our team.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 61: WHY DID SHE WRITE SUCH A LETTER?
Answer: Why was such a letter written by her?
(Double Interrogative Sentence (Wh-word + helping verb construction) – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 62: I POSTED THE LETTER.
Answer: The letter was posted by me.
(Affirmative Sentence – Past Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 63: YOU WILL HAVE TAKEN BREAKFAST.
Answer: Breakfast will have been taken by you.
(Affirmative Sentence (Prediction) – Future Perfect Tense)
Exercise 64: WHO WILL OPPOSE YOU?
Answer: By whom will you be opposed?
(Interrogative Sentence using a question (WH) word – Future Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 65: ARE YOU LISTENING TO THE NEWS?
Answer: Is the news being listened to by you?
(Interrogative Sentence – Present Continuous Tense)
Note: While some grammarians argue that “listen” shouldn’t have a passive form as it is an intransitive verb, “listened to” provides a different case. So, the sentence “Is the news being listened to by you?” seems to be correct. More passive voice exercises with answers will further make the idea clear.
Exercise 66: HE DOES NOT TAKE EXERCISE REGULARLY.
Answer: Exercise is not taken by him regularly.
(Negative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 67: GIRLS SING SONG.
Answer: Songs are sung by girls.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Indefinite Tense)
Exercise 68: THE RICH MAN IS GIVING ALMS.
Answer: Alms is given by the rich man.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Continuous Tense)
Exercise 69: THEY HAVE HEARD THE SONGS.
Answer: The songs have been heard by us.
(Affirmative Sentence – Present Perfect Tense)
Exercise 70: HE KILLED A SNAKE.
Answer: A snake was killed by him.
Also read: 30+ Advantages/Disadvantages of Fashion Essay in Detail
Exercise 71: YOU SHALL OBEY OUR ORDERS.
Answer: Our orders will be obeyed by you.
(Affirmative Sentence – Future Indefinite Tense)
Note: The sentence “You shall obey our orders” also suggests a warning, an order, or a prediction.
After going through passive voice exercises with answers and independently solving them, you might have grabbed the universal rules governing the change from active to passive voice.
Change the Voice
Universal Rules: Change from Active Voice to Passive Voice with Example Sentences from Past Papers.
1. Interchange the positions of subject and object.
فاعل کو مفعول کی جگہ پہ اور مفعول کو فاعل کی جگہ پہ لگائیں۔
2. Change the objective case of the object into subjective case. Change the subjective case of the subject into the objective case.
مفعول کی مفعولی حالت کو تبدیل کر کے فاعل کی جگہ پہ لگائیں۔ فاعل کی فاعلی حالت کو تبدیل کر کے مفعول کی جگہ پہ لگائیں۔
3. If the subject or object is a noun, its case will not be changed.
اگر فاعل یا مفعول “ناؤن” ہو تو اس کی حالت میں تبدیلی نہیں ہوگی۔
4. Use “by” before the object (objective case of subject).
مفعول سے پہلے “بائے” کا استعمال کریں۔
5. Always use the third form of the verb in passive voice sentences.
“پیسو وائس” جملوں میں ہمیشہ فعل کی تیسری فارم استعمال ہوگی۔
6. A passive voice sentence will always have a helping verb and you will always need to add one.
“پیسو وائس” جملوں میں ہمیشہ امدادی فعل کا استعمال ہوگا۔
Even if there are one, two or three helping verbs in the active voice sentence, you will still need to add an extra one. This principle applies to all the change the vice examples with answers.
Change of Pronouns – Active Voice to Passive Voice
| Subjective Case | Objective Case |
| I | Me |
| We | Us |
| You | You |
| He | Him |
| She | Her |
| It | It |
| They | Them |
While doing passive voice exercises with answers, you must pay heed to how such rules and changes express themselves.
10 Differences Between Active and Passive Voice Exercise
There are three types of voices found in languages, i.e. active, passive, and middle. English uses syntactic variations to express these distinctions of voice.
1. Subject is Doer vs Recipient
The first obvious difference between active and passive voice is that, in the former, the subject is the doer of the action. While, in the latter, the subject is the recipient or target of the action being performed.
In the example, “The government has constructed dams”, ‘the government’ (the subject of the sentence) is the doer of the action, i.e. constructing “dams”.
On the other hand, when the same sentence is converted to passive voice, i.e. “Dams have been constructed by the government”, the subject (the government) becomes the recipient or target of the action.
2. Straightforward vs Roundabout
Straightforwardness and roundaboutness mark the second major difference between active and passive voice. Active voice is the straightforward way of stating, interrogating, negating, requesting, advising or ordering something.
On the other hand, passive voice is used as a roundabout method of uttering, expressing, beseeching, asking, or conveying something.
3. Subjectivity vs Objectivity – in Passive Voice Exercises with Examples
The 3rd major difference between active and passive voice is that of subjectivity and objectivity.
In a verb or sentence that is in active voice, the personal feelings, opinions, or tastes of the doer of the action get highlighted.
On the contrary, a verb or sentence in passive voice serves to hide the sentiments, views, and beliefs of the subject.
4. Everyday vs Research Language
While everyday language mostly makes use of active voice, the research language prefers the use of passive voice. Here the usage of passive voice can help maintain objectivity which is one of the principles of research.
5. Actively vs Passively Participating
In the case of active voice, the subject seems to be actively or willingly participating in the execution of an action. On the other hand, in the passive voice, the subject is seen as passively or unwillingly taking part in the execution of the given task.
6. Focus on Subject vs Action
In the case of an active voice, the focus is on the subject of the verb. On the other hand, the focus is shifted to the action when the verb is in the passive voice.
You can understand this through semantic analysis of tanswerhe change the voice examples with answers.
7. Use of Past Participle vs Other Verb Inflections
A verb or sentence in a passive voice always takes at least one verb – the main verb – in past participle or 3rd form. However, other verb inflections may also be used.
A sentence in the active voice, on the other hand, does not necessarily require the use of a verb in the past participle.
8. Simplicity vs Complexity
Another notable difference between active voice and passive voice is that the former is based on simple rules while the latter involves a bit of complexity.
A relatively high level of complexity is evident from change to voice examples with answers.
9. More vs Less Frequent Usage
The use of active voice sentence is common in various contexts and situations. The passive voice sentences are, however, less frequently used.
Ease vs Difficulty in Construction in Change from Active to Passive Voice
Being relatively simple, the active voice sentences are usually easy to deal with. In other words, you can easily create sentences in the active voice.
The same may not be true when it comes to passive voice. Here, the rules governing the construction of a meaningful sentence are a bit complex.
For example, as you might have noticed in the change the voice examples with answers, you always use a 3rd form (past participle) of the verb and an auxiliary.
Conclusion
If you find the 70+ change the voice examples with answers useful, please share your experience in the comments section below. You are also requested to give your precious opinion for the further improvement of the content.
Pingback: 70+ Advantages of Internet in Points and Essay in Detail - TBH Product Hunt
Pingback: Score 8/8, Fast-to-Learn 9th Class English Letters Notes - The Future Hub
Pingback: All 40 - Translation Paragraph Urdu to English 10th Class - The Future Hub
Pingback: Easiest 2nd Year English Notes Book 2 Question Answer - Smart Info Hub
Pingback: English Essay on a Rainy Day for Class 10 with Quotations - Smart Info Hub
Pingback: What Is Fashion Essay with Types, Trends, and Importance - Smart Info Hub
Pingback: 12 Types of Tenses with Examples, Formula, V-Inflections - Smart Info Hub
Pingback: Essay on a Hockey Match with Quotations for 10th Class - Smart Info Hub
Pingback: Unit 2 Patriotism 9th Class Translation in Urdu, Class 9 English Notes - Smart Info Hub
Pingback: Unit 10, A World Without Books Class 10 Translation in Urdu - Smart Info Hub
Pingback: Unit 4 Hazrat Asma 9th Class Translation in Urdu, Class 9 English Notes - Smart Info Hub
Pingback: 3 Versions of The Rain Poem Summary 1st Year/10th Class - Smart Info Hub
Pingback: Unit 6 The Quaid’s Vision and Pakistan Translation in Urdu 9th - Smart Info Hub